

VOC Exhaust Gas Control: Current Eco Trend
VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds) are organic chemical compounds that vaporize and enter the atmosphere, during the process of industrial manufacturing such as home appliances, car/motorbike/bicycle painting, oil-refinery plants, evaporation of oil from petrol stations, PU plastics manufacturing, painting and solvent industries. These organic vapors are harmful to health and could be explosive. Thus VOCs have to be dealt with carefully and can not be released to the air directly.
Catalytic Incineration is the Shortcut of VOC Treatment
Catalytic incineration is effective in dealing with VOC exhaust gases. It uses highly active catalysts that can speed up oxidation of VOC and turn exhaust into non-hazardous CO 2 and H 2 O. The advantages include simple facilities, affordable operation costs, no secondary pollution (e.g. NOx, solid/liquid waste), and extremely suitable for either waste treatment of large-sized factories or non-industrial usage such as odor removal. 。
Catalytic Incineration
 |
Technical Principles |
 |
Main reaction of catalytic incineration : |

This reaction happens both with and without catalysts, but using catalysts can reduce the treatment temperature by about 250 C 。
The table below shows some common VOC exhaust gases and their combustion temperatures with/without catalysts.
| VOC Type |
Thermal Oxidizer (No Catalyst) |
Catalytic Type |
|
|
|
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
| |
|
|
|
※ Temperature is affected by exhaust gas concentration and flow rate.
 |
System Introduction
|
 |
The system design of catalytic incineration is very simple. Some major components are illustrated below: |
The heater, depends on air quantity, operation and maintenance, can make use of electricity, gas or No. 6 Oil. The heat exchanger is used to recycle heat recovery produced by VOC burning, pre-heat, air-intake and for other purposes. Similarly, it depends on exhaust gas concentration and the environment in which the machine is operated.

Catalyst Specifications:
| Model |
Catalytic Type |
Occasions |
|
|
|
| MR – J |
Spiral wound metal ¶ |
Exhaust treatment with medium/low air quantity, no acid gases |
|
| |
| MH-T |
Metal honeycomb † |
Exhaust treatment with high air quantity, no acid gases |
|
| |
| CH-U |
Honeycomb ceramic ¶ |
Exhaust treatment with high/low air quantity, medium- sized/large-sized factories, acid gas resistance, low piezoresistive |
|
| |
| CF-W |
Expanded ceramic ¶ |
Exhaust treatment with high/low air quantity, medium- sized/large-sized factories, acid gas resistance, high shape/size flexibility |
|
| |
| CP |
Granulated |
Low air quantity, exhaust (CO.H 2 ) treatment, high piezoresistive |
|
|
|
¶ The unit size of honeycomb ceramic catalysts is 15cm x 15cm x 15cm . Specifications of expanded ceramic and spiral wound mental catalysts can be customized. Practically several units can be combined to meet the need.
† The size and shape of metal honeycomb catalysts can be designed on request. Suitable for small-sized odor removal or other non-industrial machines.
Range:
|
|
 |
Can Printing |
 |
Chemical industry |
|
|
 |
Printing industry |
 |
Paint industry |
|
|
 |
Electronics, semiconductor |
 |
Coffee roasting |
|
|
 |
Magnetic Tape |
 |
Magnet wire industry |
|
|
 |
PE Film |
 |
Food Industry |
|
|
 |
Adhesive tape industry |
 |
Automotive painting |
|
|
|

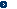
Catalyst Activation Test

 |
Depends on conditions, invalid old catalyst could be regenerated . |
 |
Ching Huei is the only company in Taiwan that owns this technology. |
 |
Effects of regeneration are cost-effective. |
Effects of Regeneration
Typical Pressure Drop of Different Catalysts
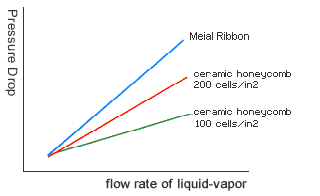

|
